The Basics of U.S. Copyright
— and How It Applies to AI
Peter Henderson, J.D., Ph.D.
Today's Roadmap
- I. Foundations — who gets copyright in what?
- II. Rights, Claims, Remedies, and Defenses — what can you do with copyrighted material?
- III. Other Considerations — DMCA • interaction with licenses/contracts
"Copyright law is the only law already in existence that could bring generative AI systems to their knees..."
Foundations
Who gets copyright in what?

Intellectual Property Clause of the Constitution
"To promote the Progress of Science and useful Arts, by securing for limited Times to Authors and Inventors the exclusive Right to their respective Writings and Discoveries."
Congressional Implementation of Constitutional Copyright Power
Copyright Act of 1976
Current law governing copyright in the United States (after several iterations) signed into law by President Gerald Ford

President Ford signing legislation at the White House
17 U.S. Code § 102 - Subject matter of copyright: In general
- (1) literary works;
- (2) musical works, including any accompanying words;
- (3) dramatic works, including any accompanying music;
- (4) pantomimes and choreographic works;
- (5) pictorial, graphic, and sculptural works;
- (6) motion pictures and other audiovisual works;
- (7) sound recordings; and
- (8) architectural works.
Duration (Post‑1978)
- Life + 70
- Works‑for‑hire/anonymous/pseudonymous: 95 from publication or 120 from creation
Panel Question
Is software copyrightable? If so, what is it protected as? What about algorithms?
Thick vs. Thin Copyright
THICK COPYRIGHT
More creative/original
THIN COPYRIGHT
More functional/fact-based
BROADER PROTECTION
NARROWER PROTECTION
Key Idea
The more creative and original a work, with many sub-parts that are independently copyrightable, the "thicker" its copyright protection. For example, in a novel, the characters, individual chapters, plot lines, might be copyrightable. You divide the book up and it has pieces that can be independently protected. On the other hand, if you have a textbook, news article, or software, the functional components or the facts might not be protected and as a result mostly the verbatim expression is protected, but others can use subcomponents more easily.
Thomson Reuters v. Ross Intelligence (2025)
Key Facts of the Case
Thomson Reuters, the owner of the Westlaw legal research platform, sued Ross Intelligence, an AI-powered legal research startup. Ross contracted out a data annotation firm to create "headnotes"—brief summaries of key legal points from court opinions—to train their artificial intelligence system. The firm, instead based their annotations off of Westlaw's headnotes. Thomson Reuters sued Ross for copyright infringement. Under dispute is both whether the headnotes are copyrightable and whether Ross's use of them is fair use.
Gemini-generated cartoon based on these facts
Thomson Reuters v. Ross Intelligence (2025)
Example Headnote
Question
"Does originality for copyright purposes mean that the work was independently created and has some minimal degree of creativity?"
West Headnote
"Originality, for copyright purposes, means that the work was independently created and has some minimal degree of creativity."
Case Opinion
"Original, as the term is used in copyright, means only that the work was independently created by the author (as opposed to copied from other works), and that it possesses at least some minimal degree of creativity."
Panel Question: Are West Headnotes Copyrightable?
✓ Arguments FOR Copyrightability?
✗ Arguments AGAINST Copyrightability?
Question
Why would this matter for AI? Think to the technical details of AI training.
Additional Exceptions to Copyrightability
Scènes à Faire
Standard, obligatory scenes that flow naturally from basic situations
"A detective story must have a crime, suspects, and clues"

Case: Cain v. Universal Pictures Co. (1942) - Court held that standard dramatic situations are not copyrightable as scènes à faire
Public Domain
Works no longer protected by copyright
"Steamboat Willie" (1928) - Mickey Mouse entered public domain in 2024
Examples: Works created before 1927, government works, works with expired copyrights
Non-Human Authorship
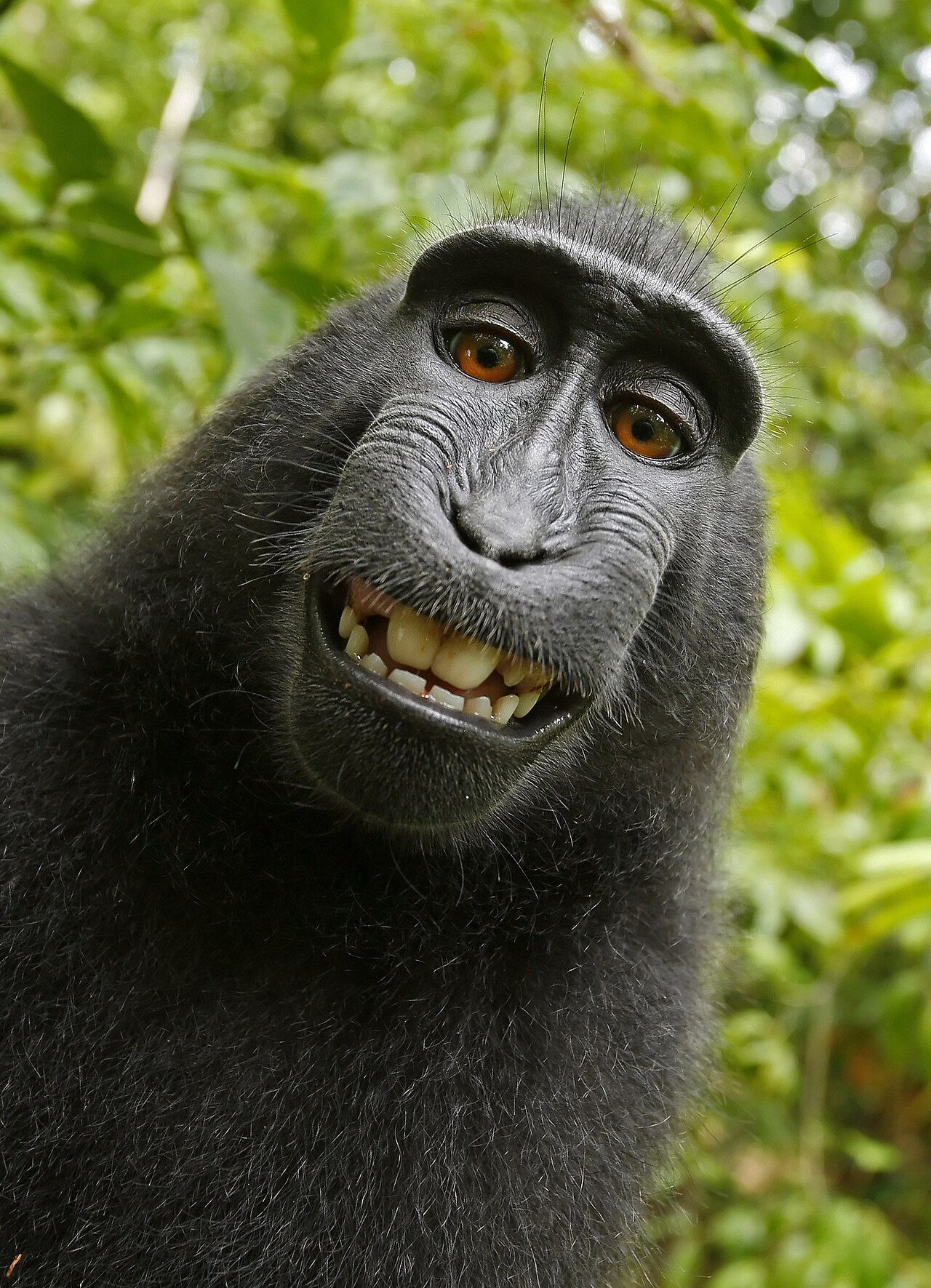

A crested macaque named Naruto took a selfie using photographer David Slater's camera. The monkey's "selfie" went viral, and PETA sued on behalf of Naruto, claiming the monkey owned the copyright. The Ninth Circuit held that animals cannot own copyrights because copyright law requires human authorship. [Case Opinion Link]
Question

What's different about Naruto taking a photo versus an AI generating content?
⚠️ What problems could arise from loosening the human authorship requirement to allow AI to be the author?
The Copyright Office's Position on AI


- Author must be human
- When GenAI in the loop, human must exert creative control and they get copyright in aspects of the work they created
- Emphasis on non-determinism of GenAI outputs being a problem
- In practice, compilation right if authors have edited model outputs significantly. Pretty much not copyrightable, if only prompt-based inputs without editing.
Panel Question
Under the Copyright Office's standard, and everything you know so far, do you think that model weights are copyrightable?
Alternative to Strict Human Authorship: "Dominant Author" or "Lion's Share" test

"Lion's share" test as an alternative
Still requires disentangling human contribution to identify if they actually contributed a Lion's Share
Alternative: "Dominant Author"
Another alternative is to consider "dominant author," like in disputes between directors and producers.
See, e.g., 16 Casa Duce LLC v. Merkin; Garcia v. Google.
But what about legitimate human contributions to AI-generated works on the input side?
Pretraining Methodology
Fine-tuning/Alignment
In-context Prompting
Memorized data
Is it actual influence? Understanding "attempts" to control outputs.

Luxi He, Yangsibo Huang, Weijia Shi, Tinghao Xie, Haotian Liu, Yue Wang, Luke Zettlemoyer, Chiyuan Zhang, Danqi Chen, Peter Henderson
- Models don't always really pay attention to prompt instructions.
- Even worse, some diffusion model APIs silently cut off prompt after 77 tokens, so it doesn't even reach the model. So claims of a long-detailed prompt being copyrightable might be misleading.
Panel Question
Are there technical methods to quantify human contributions to operationalize the "lion's share" test? Do you think they would work for court cases?
II. Rights, Claims, Remedies, and Defenses
What can you do with copyrighted material?
TBs of Training Data
Books • Articles • Websites • Code • Social Media
Most of it is copyrighted. So what could go wrong?


50 lawsuits in the United States alone (and more internationally)
Exclusive Rights (17 U.S.C. §106)
Subject to sections 107 through 122, the owner of copyright under this title has the exclusive rights to do and to authorize any of the following:
- to reproduce the copyrighted work in copies or phonorecords;
- to prepare derivative works based upon the copyrighted work;
- to distribute copies or phonorecords of the copyrighted work to the public by sale or other transfer of ownership, or by rental, lease, or lending;
- in the case of literary, musical, dramatic, and choreographic works, pantomimes, and motion pictures and other audiovisual works, to perform the copyrighted work publicly;
- in the case of literary, musical, dramatic, and choreographic works, pantomimes, and pictorial, graphic, or sculptural works, including the individual images of a motion picture or other audiovisual work, to display the copyrighted work publicly; and
- in the case of sound recordings, to perform the copyrighted work publicly by means of a digital audio transmission.
Registration
- Registration not required for protection—but needed to sue (submit the work to Copyright Office).
- Statutory damages/fees only if timely registration (§412), otherwise have to prove actual damages.
- Notice © optional post‑1989 but still helpful.
Copyright Remedies
⚖️ Direct Infringement
- Actual copying of protected work
- Violates one of the §106 exclusive rights
- Strict liability (no intent required), but there is a "volition" consideration. See Denicola 2018.
- Owner has burden to prove copying + improper appropriation
🔗 Secondary Infringement
- Contributory: Knowledge + material contribution
- Vicarious: Right/ability to control + financial benefit
- Applies to platforms, services, intermediaries
- DMCA safe harbors may provide protection
Fair Use (17 U.S.C. §107)
⚖️ Factor 1: Purpose
Commercial vs. educational, transformative use
📚 Factor 2: Nature
Creative vs. factual, published vs. unpublished
📏 Factor 3: Amount
How much was used, qualitative importance
💰 Factor 4: Market Effect
Impact on original work's market value
Harper & Row v. Nation Enterprises (1985)

Court's Answer: NO
The Supreme Court held that The Nation's use was NOT fair use. Even though only 200-400 words were used from a 200,000+ word manuscript, these words were the "heart of the book" - the most newsworthy and commercially valuable portions. The court emphasized that quality matters more than quantity in fair use analysis.
Authors Guild v. Google (2015)
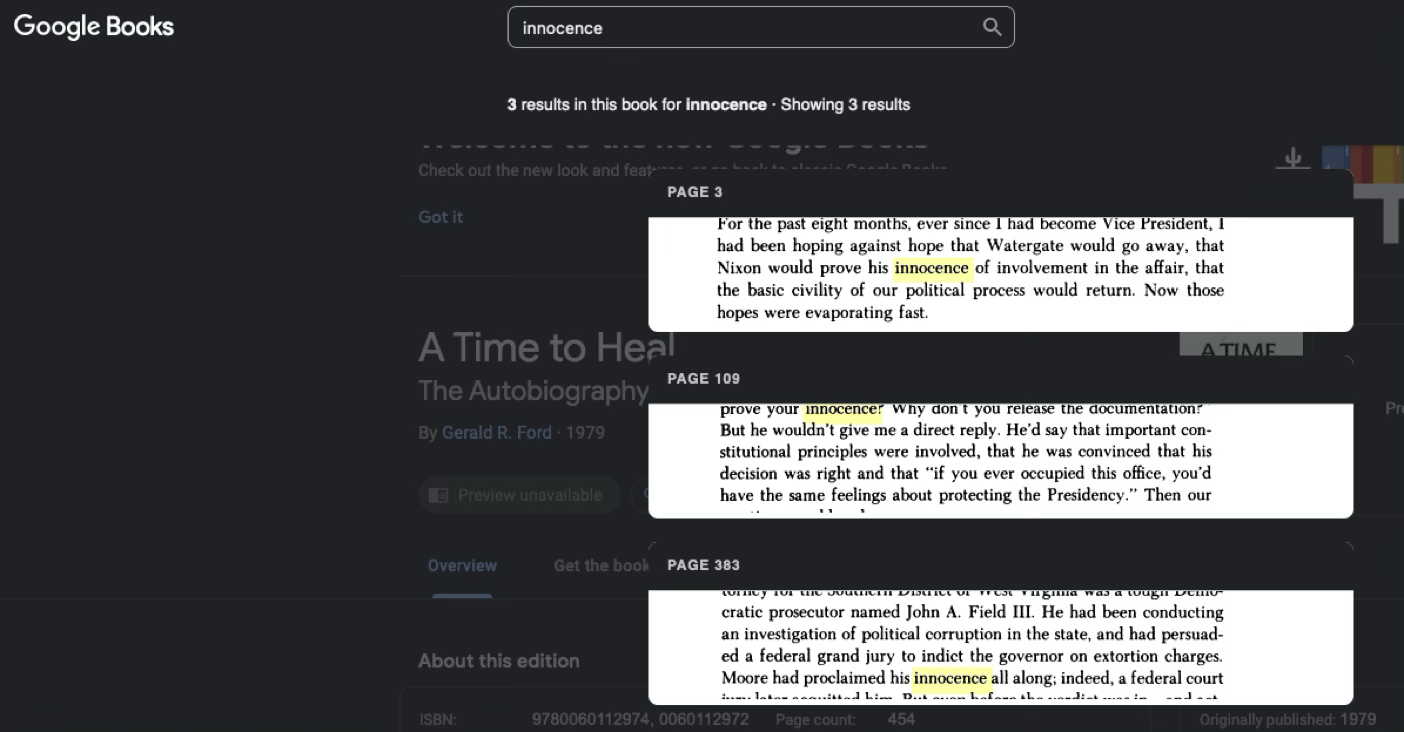
Court's Answer: YES
The Second Circuit ruled that Google's digitization and snippet display constituted fair use. The court found the use was highly transformative, serving a different purpose than the original works, and provided significant public benefits without harming the market for the original books.
Paramount v. Axanar Productions (2017)

Court's Answer: NO
The court ruled that Axanar's fan film was NOT fair use. The film closely adhered to Star Trek canon and characters, was commercial in nature, and could potentially harm the market for authorized Star Trek content. The case settled before trial.
Warner Bros. v. RDR Books (2008)
Court's Answer: NO
The court ruled that the Harry Potter Lexicon was NOT fair use. While reference works can be fair use, this lexicon copied too much creative expression and could serve as a market substitute for authorized companion books. J.K. Rowling was awarded damages.
Dr. Seuss v. ComicMix (2019)

Court's Answer: NO
The Ninth Circuit ruled that "Oh, the Places You'll Boldly Go!" was NOT fair use. The court found it was not sufficiently transformative as a parody and borrowed too extensively from Dr. Seuss's original work, including distinctive artistic style and substantial text.
Warhol Foundation v. Goldsmith (2023)
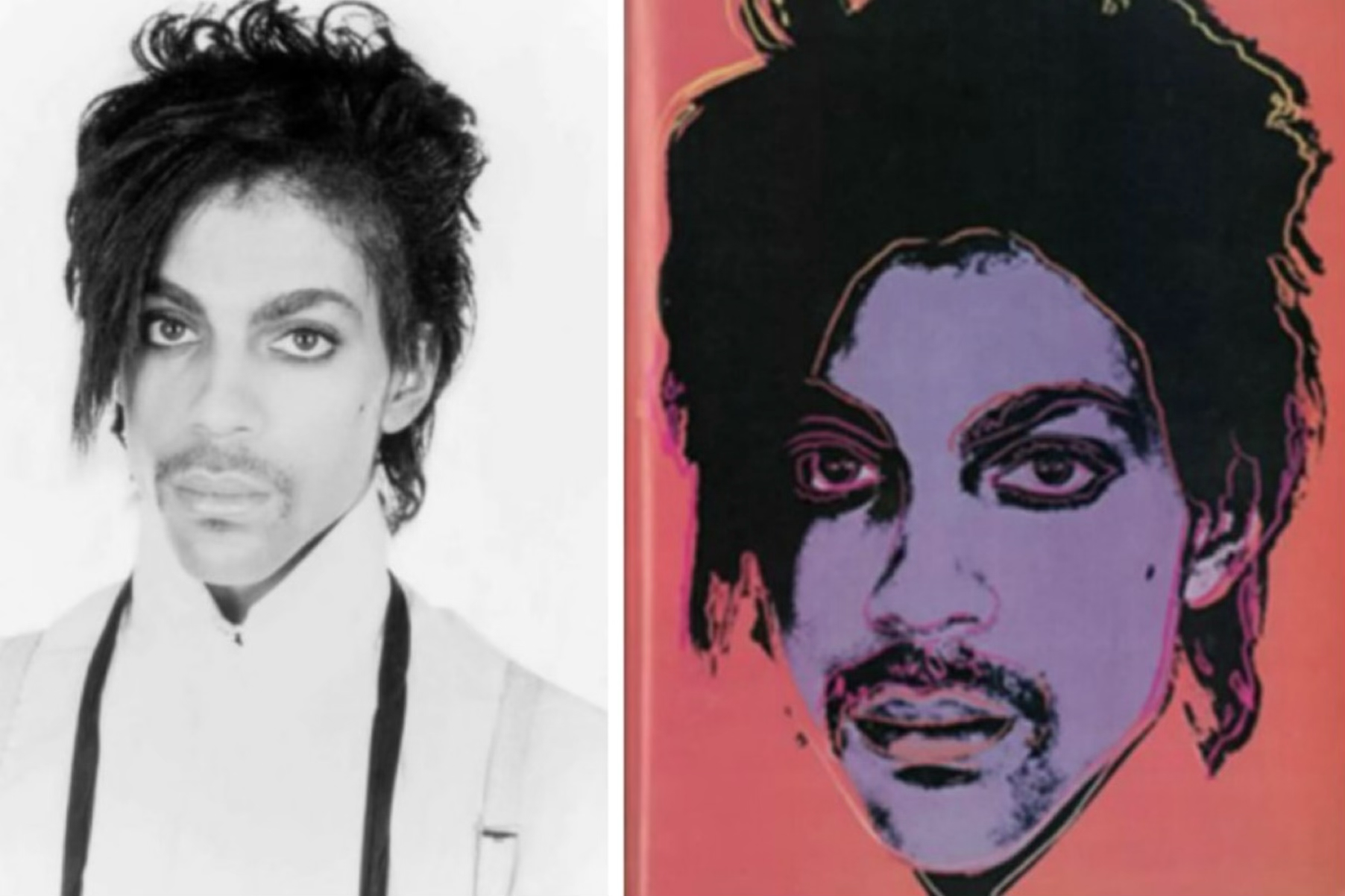

Court's Answer: NO
The Supreme Court ruled that Warhol's Prince series was NOT fair use. The Court emphasized that "transformative" isn't magic - both works served similar purposes (portraits of Prince) and competed in the same market. This case significantly narrowed transformative use.
Solid Oak Sketches v. 2K Games (2020)
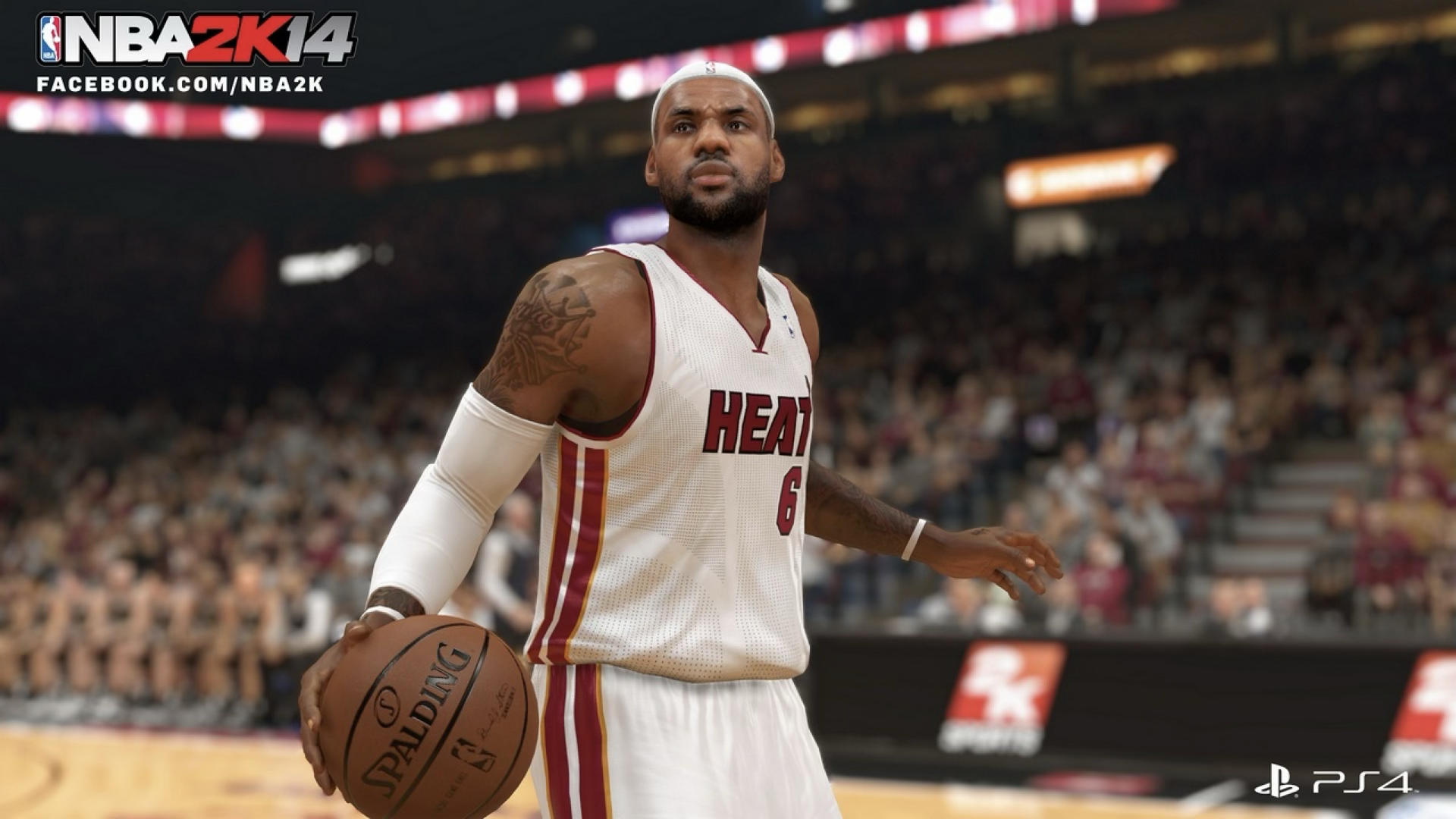

Court's Answer: YES
The court ruled that 2K's use of player tattoos was fair use. The tattoos were de minimis (incidental and small), served a different purpose than the original tattoo art, and did not harm the market for tattoo designs. The court emphasized the tattoos were not the focus of the game.
Alexander v. Take-Two Interactive (2022)

Court's Answer: NO
The jury ruled that Take-Two's use of Catherine Alexander's tattoos on Randy Orton in WWE 2K was NOT fair use. Unlike the NBA 2K case, the court found the tattoos were prominently displayed and served the same decorative function in the game as in real life. Alexander was awarded $3,750 in damages.
Kadrey v. Meta Platforms (2023)

Bartz v. Anthropic (2023)

UMG v. Anthropic (2023)

Can models really output training text?

Foundation Models and Fair Use, Journal of Machine Learning Research (2023).
Weighing fair use factors in foundation model cases?
Key consideration in Google Books were the mitigation strategies in place preventing use of the service as free access to books.
Non-literal infringement makes mitigations challenging though
Between Labor Protection and IP Rights


Discussion Questions:
What do you think? Should we be considering impacts on labor markets when crafting IP policy?
Argue for or against incorporating labor market considerations into intellectual property law.
III. Other Considerations
DMCA Safe Harbor and Interaction with Licenses and Contracts
So why aren't platforms sued endlessly?
ORIGINS OF DMCA § 512
Court in 1995 decided RTC v. Netcom:
Facts: RTC sought to hold Netcom, an Internet access provider, strictly liable for infringement of Scientology texts posted on a bulletin board service (BBS).
Court's Holding: Court rejected strict liability theory because it would extend copyright liability too far; only volitional acts by humans trigger copyright's reproduction right. But, after notice, Netcom had a duty to investigate and take down infringing materials.
DMCA Safe Harbor
DMCA, in section 512, provides safe harbors for:
- (a) Transitory digital network communication
- (b) System caching
- (c) Hosting by service providers
- (d) Search engines
DMCA "Take down": To obtain shelter, the service provider must:
- Provide a notification and removal mechanism
- Inform users of the take down policy
What about a DMCA for AI?
⚠️ DMCA is unlikely to apply to most AI systems, since AI models are not really platforms.
- What do you think are the key challenges in applying DMCA to AI systems?
- How do you think we could address them?
DMCA § 1202
Copyright Management Information
17 U.S. Code § 1202 - Integrity of copyright management information
(a) FALSE COPYRIGHT MANAGEMENT INFORMATION
No person shall knowingly and with the intent to induce, enable, facilitate, or conceal infringement—
- (1) provide copyright management information that is false, or
- (2) distribute or import for distribution copyright management information that is false.
(b) REMOVAL OR ALTERATION OF COPYRIGHT MANAGEMENT INFORMATION
No person shall, without the authority of the copyright owner or the law—
- (1) intentionally remove or alter any copyright management information,
- (2) distribute or import for distribution copyright management information knowing that the copyright management information has been removed or altered without authority of the copyright owner or the law, or
- (3) distribute, import for distribution, or publicly perform works, copies of works, or phonorecords, knowing that copyright management information has been removed or altered without authority of the copyright owner or the law, knowing, or, with respect to civil remedies under section 1203, having reasonable grounds to know, that it will induce, enable, facilitate, or conceal an infringement of any right under this title.
DMCA § 1202 Examples
Copyright Management Information in Practice
Adding License Information
Copyright Preemption and Licensing
Earlier we discussed that models might not be copyrightable, but companies nonetheless license them.

The Preemption Problem
But this creates a problem called copyright preemption. That is: copyright says you shouldn't be able to own this thing, but you try to own it anyways through a contract.
Since contracts are state law, federal law could preempt (recall our discussion of federalism in the first class). There's a circuit split on this issue, but just know that they might not be enforceable, depending on the facts and the jurisdiction.

Panel Question
From a policy perspective, should AI model licenses be enforceable if the models themselves are not copyrightable? How could doctrinal developments in preemption around AI licensing impact AI development in other ways?
Wrap‑Up
- AI is straining copyright doctrine and forcing courts to revisit first principles—especially the labor/originality distinction.
- The lawsuits won't stop unless Congress creates a DMCA-like safe harbor for AI.
- Questions of copyrightability, federalism, and contract law all spin out from the basic uncertainty about AI and copyright.
or copyright law will "bring generative AI systems to their knees."
— Pam Samuelson